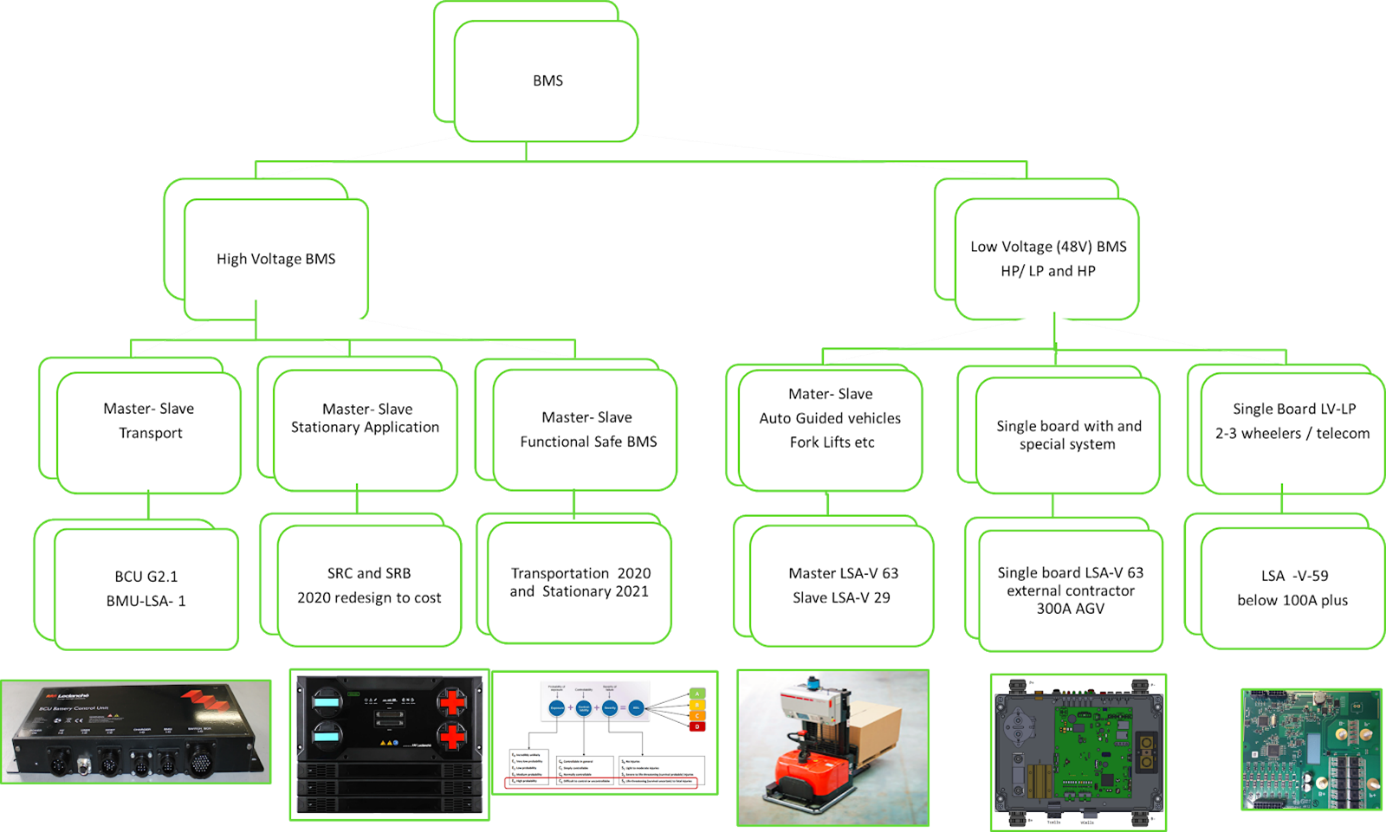
Battery Management System
Leclanché offers multiple battery management system (BMS) technologies.
BMS are an integral part of Leclanché’s high voltage (e-Transport, Stationary) and low voltage systems solutions. Leclanché develops its own in-house BMS, in partnership with a hardware company. All BMS are either master-slave or single board architecture. BMS commonly provides software and hardware safety for overcharge/ deep discharge, over/under voltage, over current, over/under temperature, pre-charge, short circuit and other protection. They have built-in technology and specific algorithms such as SOC, SOH, cell/ module balancing and real time control over charge/ discharge current. They also have the capability to indicate performance and monitor control parameters. A user-friendly Graphical User Interface (GUI) provides system performance and diagnostics for the system. BMS provides CAN and RS485 communication ports to connect to the host/ higher layer system.
Download technical data sheet.
High voltage BMS
Leclanché offers two high voltage battery management systems with 1000-V isolation: G2 for e-Transport solutions, and A1 for stationary solutions. Both have master-slave architectures and comply with design and industry safety standards. BMS offer pre-charge control, contactor control, and emergency stop and override control with system isolation fault monitoring.
BMS for e-Transport Solutions
To learn more about our e-Transport solutions, click here.
The e-Transport BMS consists of three parts:
- Master: the main BMS controller – BCU
- Slave: the module measurement units – BMU
- The contactor module – the switch box
Master – BCU
The BCU is the central control unit that monitors and controls the status of the batteries, including system charging, discharging and host communication. The BCU can be configured and integrated into the customer battery system via CAN or serial communication interfaces.
Slave – BMU
The BMU is the local voltage and temperature measurement unit for the battery modules. It sits in the module. The BMU monitors up to 12 or 24 individual cell voltages and up to 2 to 4 cell group temperatures depending on the model. The measurements are transmitted to the BCU via the internal RS485 BUS. The BMU also contains passive cell balancing circuitry controlled by the BCU to bring all cells in the module and battery to equal capacity. Multiple BMUs can be daisy-chained for a maximum system voltage of 1000VDC.
BMS data communication architecture and diagnostics tool
A diagnostics tool provides system and cell-level information, error handling, master and slave firmware updates, system configuration and parameter management, signal logging and visualisation.
BMS for Stationary Solutions
To learn more about our stationary solutions, click here.
Leclanché’s Stationary business offers solutions for small (500kWh) to mid-size (50MWh) grid connected, microgrid, solar/wind integrated and behind the meter energy storage systems. We provide stationary racks with LTO and NMC- G cell technology and complete system containers with inverter partners.
The complete BMS, or string controller (Storage Rack System), has master and slave architecture and consists of the following:
- Master SRC2 (Storage Rack Controller): Control unit of the battery storage system and separator for disconnecting the battery voltage to the outside if necessary
- Slave: SRB (Storage Rack Battery): Battery module with integrated battery management system
- SRS roof fans: Each cabinet is equipped with a rooftop fan for cooling of the battery modules during operation
- Pre-charge resistor: Pre-charge resistor to limit inrush current when connecting to a load with capacitive input
Slave (SRB)
The SRB monitors cell voltage, temperatures and balancing status of the cells via CAN to masters. Each slave is connected via signal heartbeat, which provides a third layer of safety beyond software intervention. The SRB provides all statistical data on max and min cell capacity state of charge, voltage and temperatures.
These SRB are compliant with EMC and safety industry standards (EN61000-6-2, EN6100-6-4, EN 61010-1 EN50272-1) and UN 38.3.
Master (SRC2)
The Storage Rack Controller (SRC2) is a control unit. The controller communicates and controls the connected battery modules. It provides the power to slave system (SRB). A pre-charge resistor connected in the system provides limited current for initialising the charging process through the inverter. The SRC2 controls the roof fan and monitors its function through the reported back speed signal. Leclanché’s “Slave protocol – CAN” or “Slave protocol – Modbus / TCP” are available to communicate with the host device.
Low voltage BMS
Leclanché develops low voltage BMS solutions for 24/48 volt battery modules. These BMS solutions are single board and master/ slave for multiple applications like Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and 2-3 wheelers. A low current BMS offers shunt and MOSFET on board and comes in a highly compact design. A high current BMS, on the other hand, is provided with an optional control panel with contactor control.
Each BMS has a built-in algorithm for state of charge and state of health, diagnostics tool, GUI, CAN communication ports and accurate sensors for monitoring voltage and temperature.
Boards typically have 100V isolations.